Anticonvulsant drugs
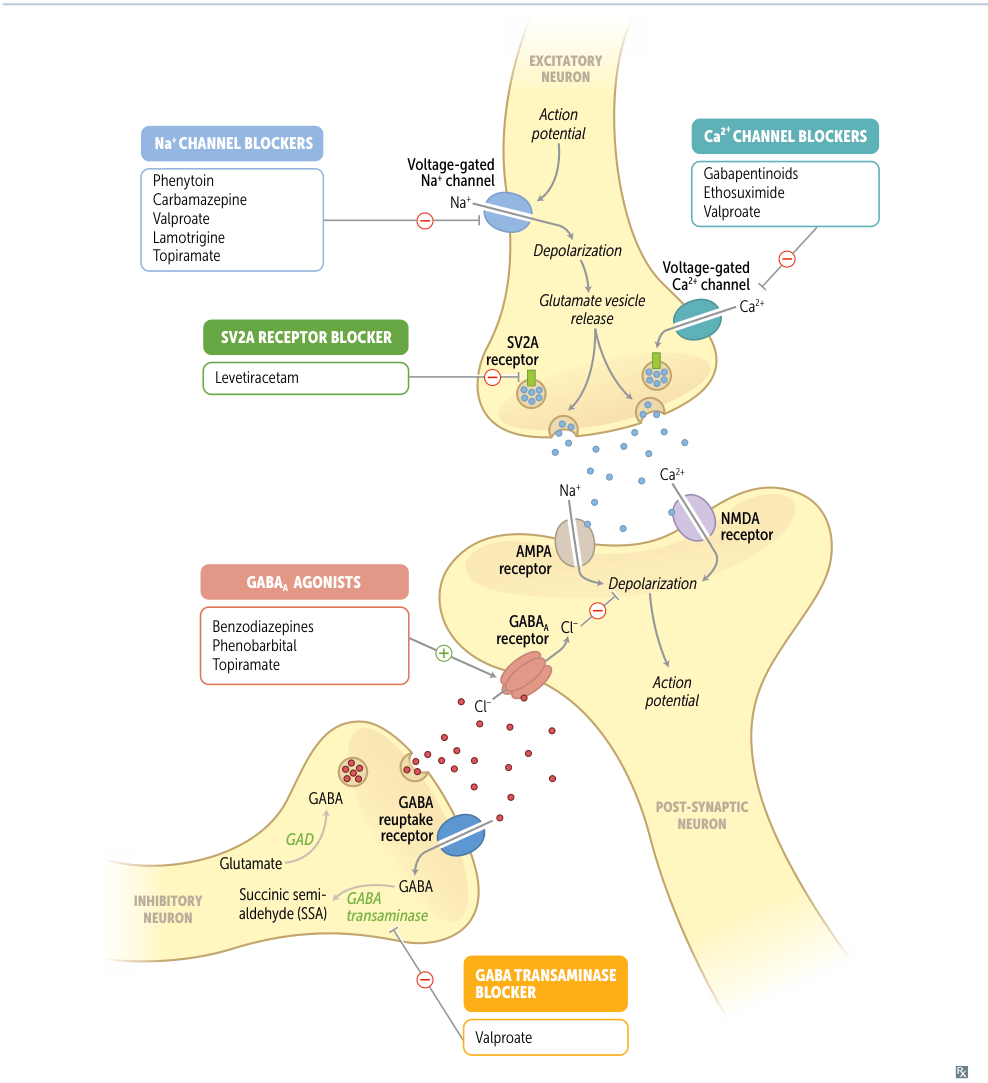
| Drug | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|
| Benzodiazepines, Phenobarbital | ↑ GABA A action |
| Levetiracetam | Inhibits vesicle fusion by binding SV2A proteins |
| Valproic Acid | Blocks Na+ channels & blocks GABA transaminase & blocks Ca2+ channels |
| Ethosuximide | Blocks thalamic T-type Ca2+ channels |
| Phenytoin, Carbamazepine, Lamotrigine | Blocks Na+ channels |
| Gabapentin | Blocks Ca2+ channels |
There are generally 5 types of seizures
- Generalized onset
- Generalized tonic-clonic seizure
- Febrile seizure
- Absence seizure
- Focal seizure
- Psychogenic non-epileptic seizures (PNES)
First-generation anticonvulsants
Carbamazepine
- First-line treatment for focal seizures
- First-line treatment of trigeminal neuralgia
- Second-line treatment for generalized tonic-clonic seizures
Mnemonic
CBZ = Cranial nerve pain, Bipolar disorder, and seiZures
Valproate (Valproic Acid)
Indication
- First-line long-term treatment for tonic-clonic generalized seizures
- Partial (focal) seizures
- Absence epilepsy
- Treatment of established status epilepticus
- Myoclonic seizures
- Migraine prophylaxis
- Bipolar disorder
Tip
Used as both as an anticonvulsant and a mood stabilizer.
Mechanism of action
- Inhibits GABA transaminase → ↑ GABA → ↓ neuronal excitability
- Inactivates Na+ channels and Ca2+ channels
Adverse effects
- Tremor
- Alopecia
- Teratogenicity
- Impairs folate metabolism, leading to neural tube defects (contraindicated in women of childbearing age/pregnancy)
Phenytoin
Adverse effects
- Phenytoin toxicity is mainly characterized by CNS manifestations. Its effect on the cerebellum and vestibular system can cause ataxia and nystagmus.
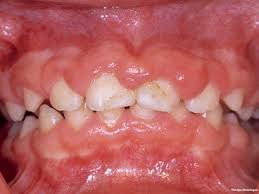
- Long-term therapy with phenytoin may cause gingival hyperplasia, coarsening of the facial features, and hirsutism.
- Phenytoin interferes with the metabolism of folic acid and may cause megaloblastic anemia.
- Phenytoin induces the P450 cytochrome oxidase system. It increases the metabolism—and therefore decreases the blood level—of many medications.
- If taken during pregnancy, phenytoin may cause fetal hydantoin syndrome.
Second-generation anticonvulsants
Lamotrigine
Indication
- First-line treatment for long-term therapy of focal seizures
- Second-line treatment for generalized seizures and absence seizures
- Mood stabilizer for treatment of bipolar disorder
Mnemonic
Use lamotrigine when your patients feel less like a lion and more like a lamb.
Lamotr-itch-gine can cause itchy rashes.
Mechanism of action
- Inhibition of voltage-gated Na+ channels → ↓ glutamate release
Adverse effects
- Rash, exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome (slow titration is necessary to prevent skin and mucous membrane reactions)
- Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
Gabapentinoids
- Pregabalin
- Drug combination for long-term treatment of focal seizures
- Neuropathic pain
- Neuralgia after herpes infection
- Gabapentin
- Second-line treatment for focal seizures
- Postherpetic neuralgia
- Peripheral (poly)neuropathy
Mechanism of action
- Inhibition of presynaptic P/Q-type Ca2+ channels via action on the α2δ-subunit → ↓ Ca2+ intracellular flow → ↓ glutamate release
Topiramate
Indications
- Focal and generalized tonic-clonic epileptic seizures
- Migraine prophylaxis
- Idiopathic intracranial hypertension
Mechanism of action
- Blockage of voltage-gated Na+ channels
- ↑ GABA
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Classic anticonvulsants (especially carbamazepine and sodium valproate!) should be avoided if possible → teratogenic effects